Design for Manufacturing
Purpose: To design parts, assemblies so they’re easy, cost-effective, and reliable to manufacture.
Minimize Part Count
- Tooling Setups , Fasteners, Assembly Time, Lower Inventory
Standardize Materials and Manufacturing Process
- Off the shelf materials + Select on: How strong? Thermal properties, how heat resistant? What colour? Insulator or Conductor?
- Standardized Manufacturing process for your part volume
- Low Volume: 3D printing, CNC Machining, Machine Shop
- High Volume: Injection, Die Casting, CNC, Sheet Metal, Extrusion, Stamping, Forging, Casting
Tolerance Parts Appropriately
- Only specify tight tolerances when required, depends on application (0.01mm)
- High Tolerance: CNC spindle shaft application: Rotates cutting tool, critical surface where shaft slides on roller bearings.
- Weak tolerances = runout = vibration.
- High RPM with small radial runout = high force on bearings
- Part being machined is inaccurate. Radial runout = wobble of turn, Axial runout = up and down motion
- Low Tolerance: Sheet Metal bracket to fasten a control panel.
- Holes and bend angle can have low tolerances because hole misalignment will not cause issues with clearance holes
Why Does Tolerancing Affect Cost?
- Requires more expensive equipment
- Slower spindle speeds to avoid deflection and vibration = more time
- Custom fixtures required, off the shelf vices won’t do the job
- Post processing inspection = increased time
- Reject rate increases = wasted time and material
- Requires specialized machinists
Self-Locating Features
- Such as bosses, tabs and chamfers that guide assembly and fixturing
Design for Process Selected
- Align holes, reuse fixturing points, and use symmetrical features
Capstone
Base Plate: Standard steel material 201 annealed steel
- Available for easy purchasing
- Great machinability due to its reduced hardness (cleaner holes, less chatter marks or burns)
- Cheapest option
Pinion and Gears
- No available gears to purchase – CNC or 3D print
- 3D printing option was selected due to budget limitations
- Selected carbon fiber nylon for its strength to weight ratio, and it is the strongest material available at the print shop
- Our module of 1.5mm was large enough for good 3D printing quality after printing small prototypes
Arm and Links
- Used off the shelf available material 6061 aluminum and made the design as simple as possible
End-Effector
- Made one solid part to reduce the quantity of parts and eliminated any additional fasteners
- Designed for CNC machine as internal holes were lined up with the external holes to make them accessible
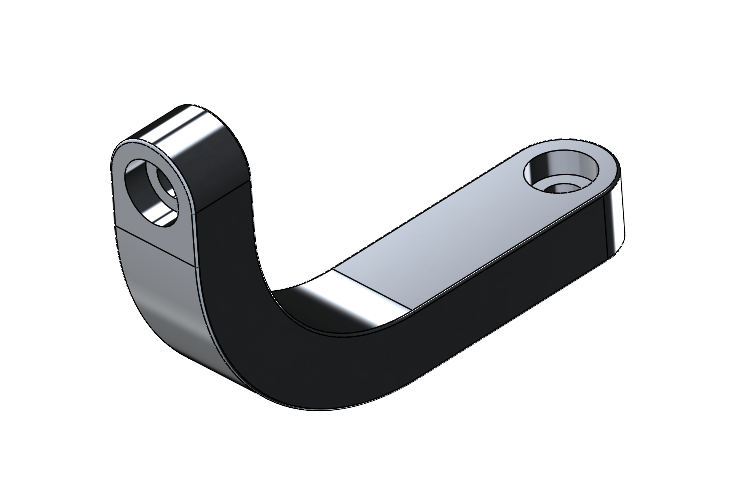
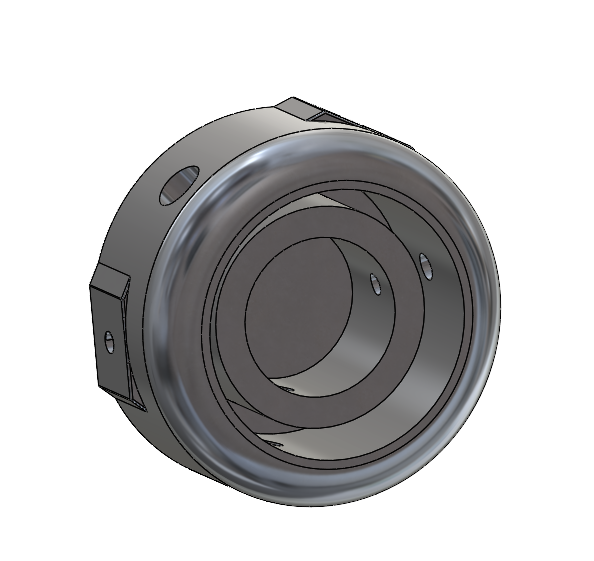

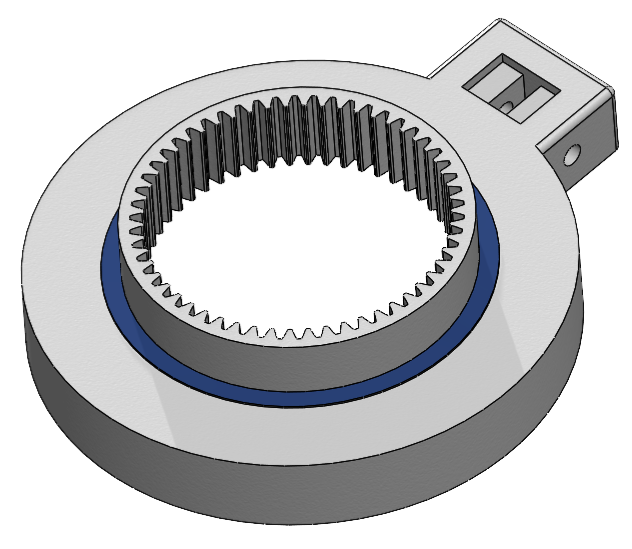
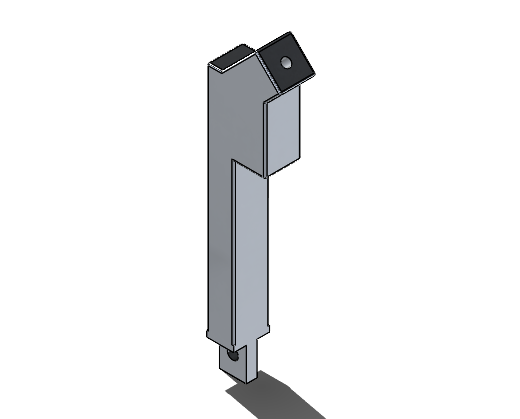


MRI Bed
- Designed all parts to be manufactured in house via bandsaws, 3 axis CNC machine, Drill press, and hand tools
- 3D printed parts designed, or spliced for build volume restrictions
UW Robot
- Chassis and parts are 3D printed
- Designed parts in accordance with manufacturer’s guidelines -> Build Size (780x780x530), Wall thickness (0.8mm), Embossed and Engraved details, and Tolerances 0.3mm
Design for Assembly
Purpose: To design parts, assemblies so they’re easy and time-efficient to manufacture.
Minimize Part Count
- Aim to use multi-functional components
- For each component, ask yourself “is this part necessary at all?
- Can a part’s primary function be performed by another part already in the assembly
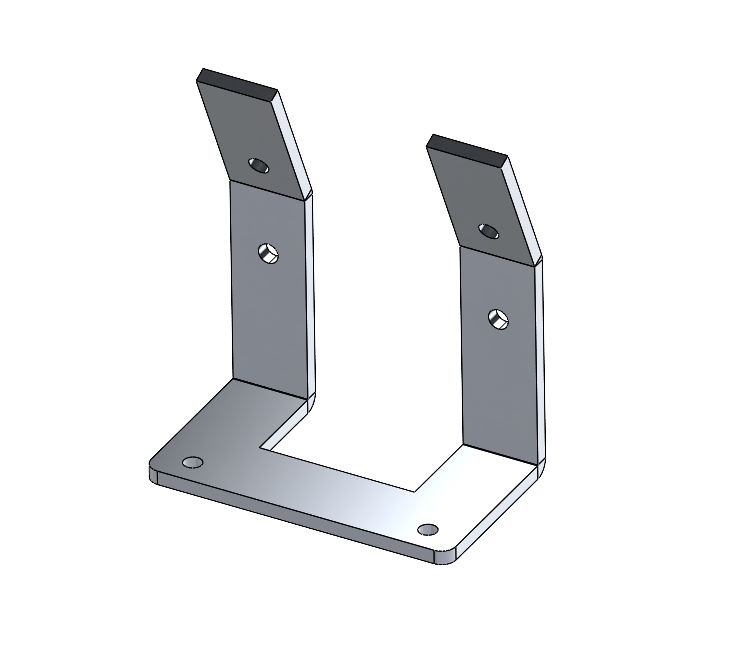
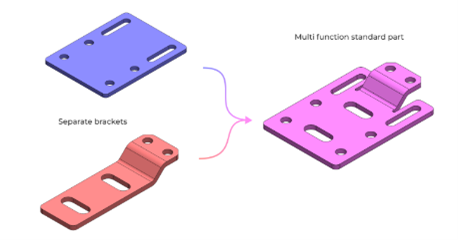

Reduce Fastener Types & Counts
- Favor snap fits over screws. If screws are appropriate, limit sizes used.
Self‑Locating & Self‑Fastening Features
- Incorporate chamfers and lead‑ins so parts naturally align and latch without external fixtures.
Design for Handling
- Ensure parts are big enough and shaped for easy pick up by hand or robot gripper; avoid tiny, delicate pieces that require tweezers.
Minimize Assembly Operations
- Strive to eliminate non value added steps: no reorientation, no secondary tooling changes, no adhesives or curing steps unless essential
- Top-Down Assembly, use gravity

Symmetry & Orientation Control
- Wherever possible, use symmetrical parts or keyed features so components can’t be installed backwards.
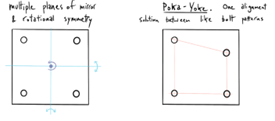
Capstone Project:
- Easy Stackable Design. Uses an orientation with gravity to easily assemble.
- Standardized the same M6 screws for all arms and links.
- Hole to identify location of long link, as it is a fraction of a millimeter different.
- No adhesive curing steps
- PVC tube arm screws accessible after installation.
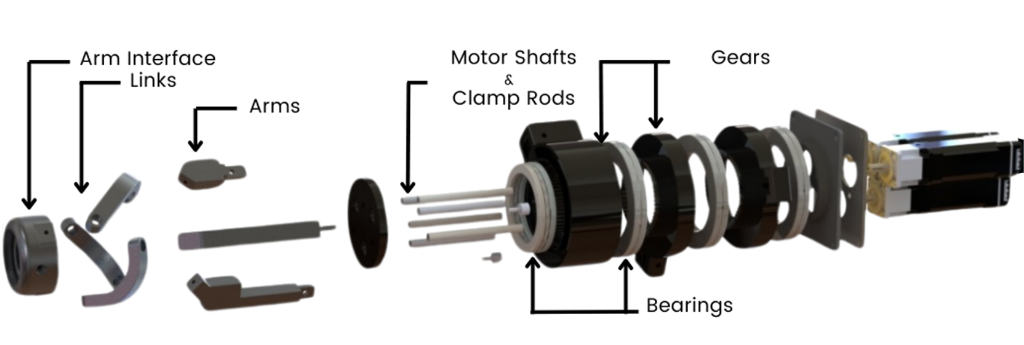
MRI BED:
- Designed for assembly and disassembly (installation) to the scanner.
- All fasteners outside the scanner, designed as an attached one unit piece, so easy slide out.
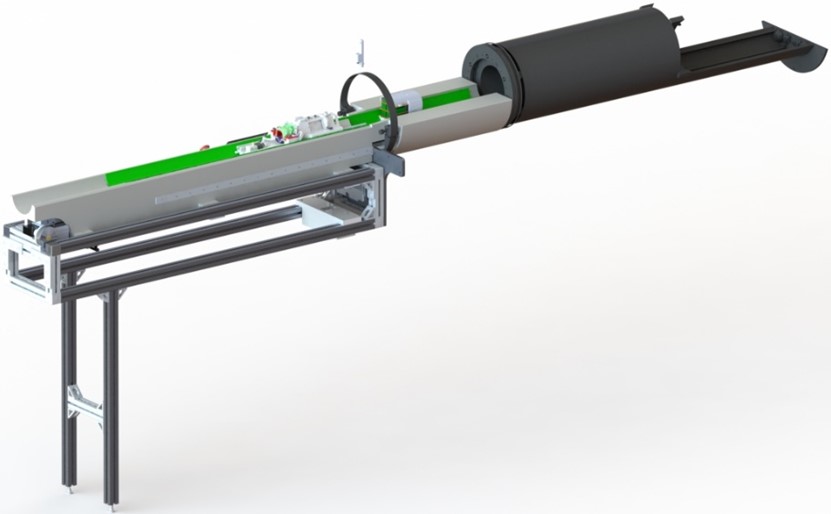

Filter Prototype:
- Minimized all fasteners.
- Modular, and Stackable design, easy assembly.
- All filters have symmetry so there is no incorrect orientation available for stackable design.
